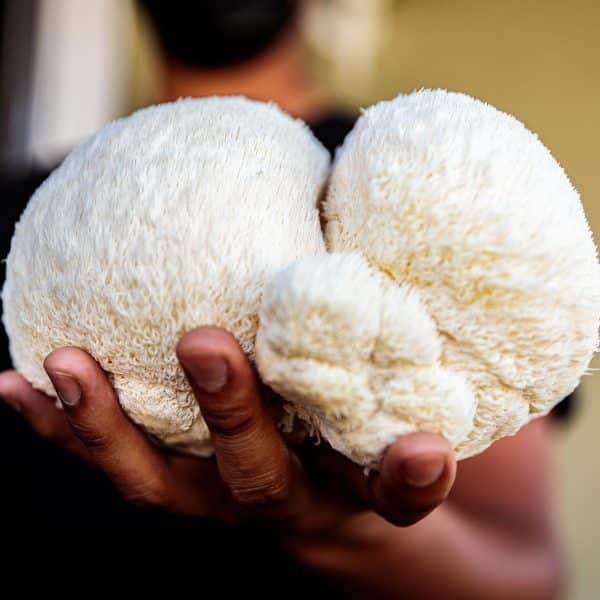
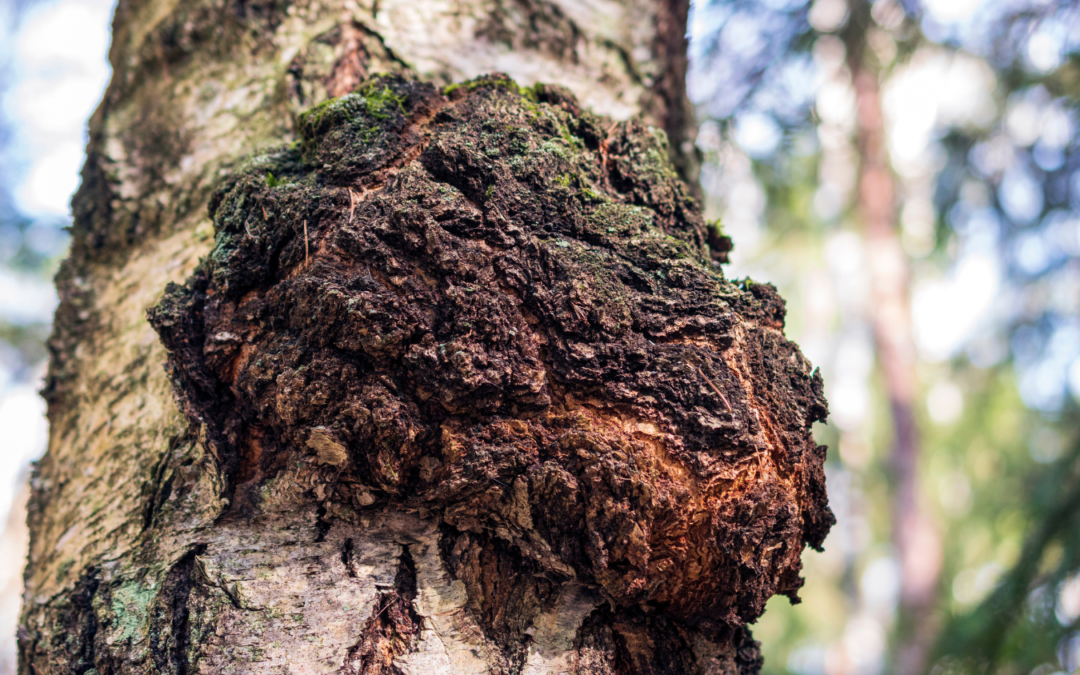
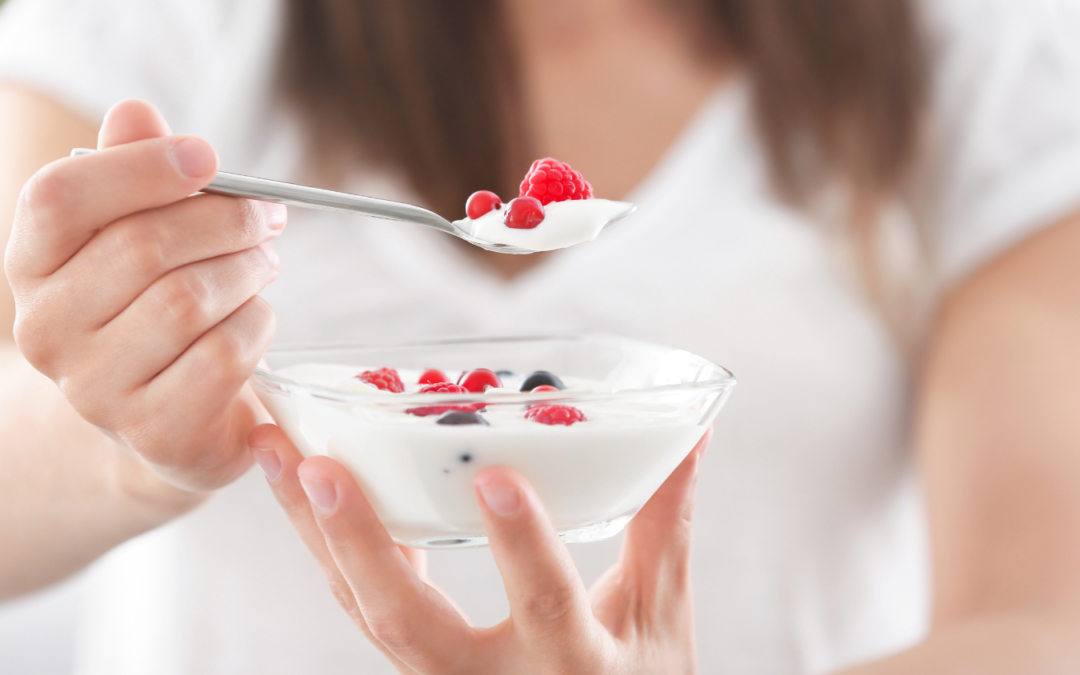
Biological value refers to the degree and efficiency with which the body absorbs, utilizes and uses nutrients from the food we consume. High bioavailability indicates that a food contains nutrients that the body can easily absorb and utilize to meet its needs. This concept is particularly relevant when it comes to protein, as high-biovalue proteins contain essential amino acids that the body cannot produce itself.
Foods with high biovalue include animal sources such as eggs, milk, meat and fish, as they often provide all the necessary amino acids in the right proportion. Plants can also have high biovalue depending on the combination of protein sources. Understanding bioavailability is important to optimize the diet and ensure that the body gets the necessary nutrients in an efficient way.